A new study led by Prof. Meital Reches of the Hebrew University with Mr. Daniel Boas, a Ph.D. student in her group and team of collaborators, has pioneered a new drug delivery system centered on switchable peptide-stabilized emulsions.
This innovation holds the promise of transforming drug delivery by allowing the simultaneous transport of both water-soluble and water-insoluble compounds within a single carrier, overcoming previous limitations in conventional methods. The findings are published in the journal Chem.
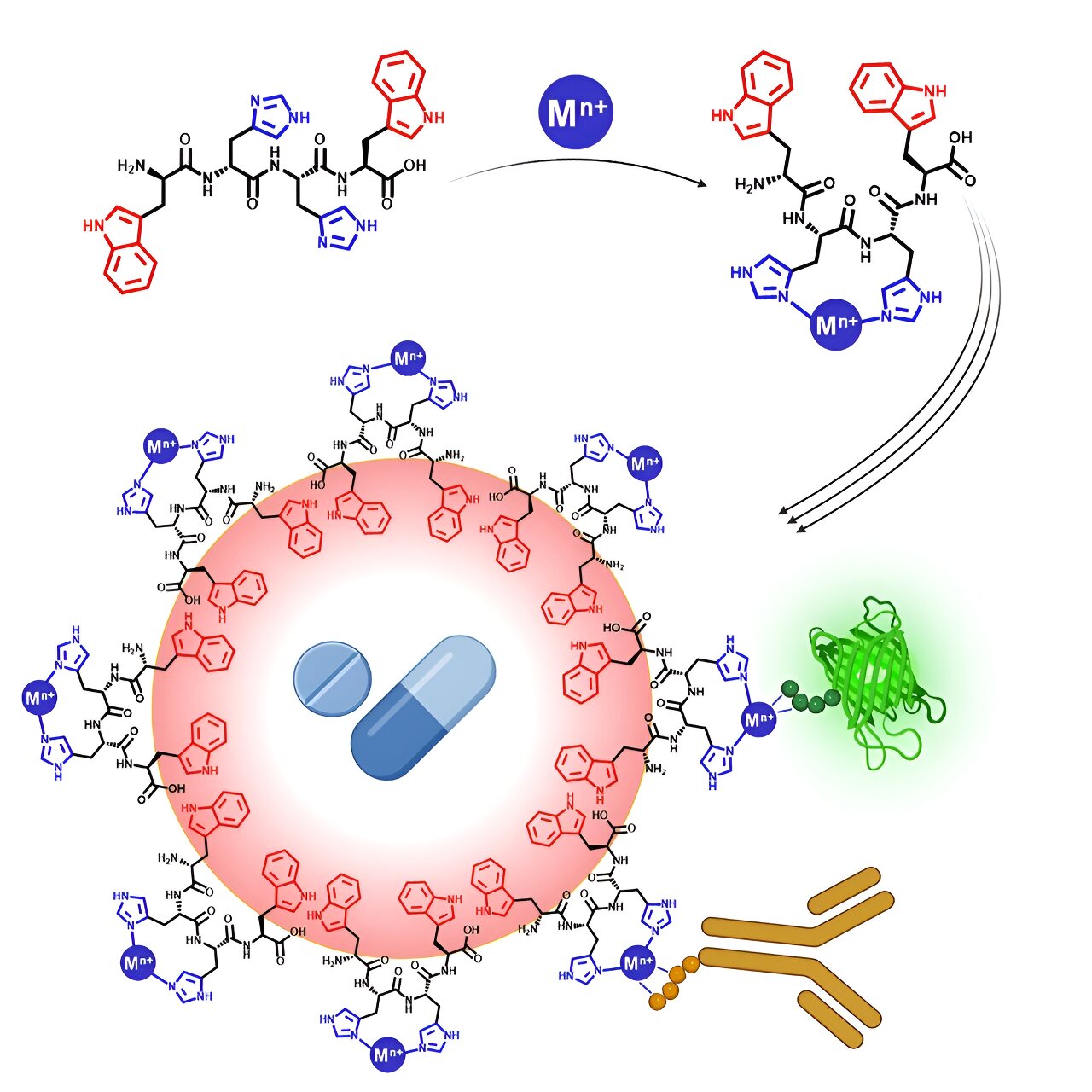
Traditionally, emulsions have served as reliable carriers for drug delivery, but their efficacy was hindered by the inability to encapsulate both types of drugs within the same vehicle. Prof. Reches’ team tackled this challenge by devising a short peptide composed of only four amino acids, capable of stabilizing emulsions and accommodating both hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds.
The heart of this innovation lies in the peptide’s remarkable ability to alter its shape upon binding specific metal ions, transforming from hydrophilic to amphiphilic. This molecular metamorphosis not only stabilizes emulsions containing water-insoluble drugs but also facilitates the delivery of water-soluble metal ions attached to the peptide.
In simpler terms, the peptide can adjust its form when it binds to certain metal ions, allowing it to adhere to both water and fat, thereby maintaining the stability of the drug mixture. Additionally, it can transport metal ions that dissolve in water.
To understand the workings of these emulsions, researchers utilized sophisticated techniques such as spectroscopy, NMR, and molecular dynamics. Their investigations revealed that the stability of these emulsions stems from bonds between histidine and metal, which can be reversible under low pH conditions, such as those found in tumor cells, thereby releasing drugs precisely where needed.
Early trials involving paclitaxel-loaded emulsions have yielded encouraging results, demonstrating significant efficacy against cancer cells. Moreover, this versatile system offers more than just drug delivery—it can be tailored with various features, opening up avenues for novel applications and benefits.
More information:
Daniel Boas et al, A multifunctional drug delivery system based on switchable peptide-stabilized emulsions, Chem (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2024.02.003
Journal information:
Chem
Provided by
Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Citation:
Drug delivery innovation: Multifunctional system based on switchable peptide-stabilized emulsions (2024, April 9)
retrieved 9 April 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-drug-delivery-multifunctional-based-switchable.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.