Study population
The study participants were randomly selected form individuals who visited the Centre of Reproductive Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, between June 2021 and December 2022. The participants consisted of individuals with health semen quality and patients diagnosed with astheno. To ensure comparability, the two categories were matched based on age frequency.
Both the health semen samples and the astheno semen samples met the following criteria: (1) Semen volume greater than 1.5 mL; (2) Semen pH value ranging from 7.2 to 7.8; (3) Sperm concentration equal to or higher than 15âÃâ106 cell/mL; (4) Liquefaction time of no more than 30 min; (5) Color of the semen: gray-white or light yellow; (6) Total sperm motility, which includes progressive (PR) and non-progressive (NP) motility, of the health semen had to be greater than 40%, with PR motility equal to or greater than 32%. In contrast, the astheno group had PR motility less than 32%. The inclusion criteria for the study were as the followings: (1) Males between the ages of 18 and 45; (2) No history of severe or significant environmental exposures such as heavy smoking, exposure to chemicals, or pesticides. The exclusion criteria were as the followings: (1) Individuals with a history of severe reproductive system trauma; (2) Long-term use of steroid drugs or medicines that affected sperm function; (3) Individuals with severe necrospermia, azoospermia, or cryptorchidism.
A questionnaire was used on-site to collect general and clinical data of the subjects, including name, age, smoking, drinking (alcohol consumption), medication history, sampling time, and abstinence days.
Semen sample collection and treatment
The semen samples were collected through masturbation after abstinence of 3â7 days. The samples were kept warm at a temperature between 20 and 37Â â and were tested within 1 h. Semen is a mixture of sperm and secretions from the male reproductive organs. Sperm accounts for about 5â10% of the total ejaculate volume, while the remaining 90â95% (referred to as seminal plasma) primarily consists of water, proteins, polypeptides, carbohydrates, enzymes, inorganic salts, and organic small molecules. These components play crucial roles in sperm function and offer potential biomarkers for assessing male fertility. The testicular barrier effectively isolates and maintain the stability and specificity of seminal plasma components. Therefore, complete semen samples, which include both seminal plasma and sperm, were used for semen quality analysis and proteomics analysis in this study.
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) activator (lificiguat, YC-1, Selleckchem, USA) has been shown to completely suppress the expression of HIF-1α under hypoxia condition20. On the other hand, Cobalt chloride (CoCl2, Mackin, China), a chemical hypoxia mimetic, can create a hypoxic environment and induce the accumulation of HIF-1α, inducing hypoxic damage in various cell models in vitro21. In this study, YC-1 and CoCl2 were used to incubate human semen samples to explore the effects of HIF-1α on autophagy and elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
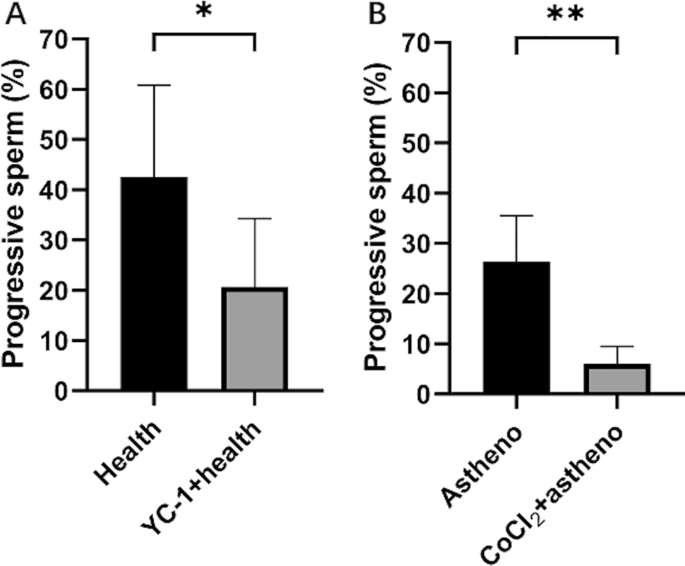
A total of 85 qualified semen samples were included in the study and divided into 4 groups. The 41 samples of health semen were further randomly categorized into a health control group (Health, 20 samples) and a health experimental group (YC-1â+âhealth, 21 samples). Similarly, the 44 samples of asthenozoospermia semen were divided into astheno control group (Astheno, 22 samples) and astheno experimental group (CoCl2â+âastheno, 22 samples). According to the results of our pilot study, the semen samples of YC-1â+âhealth group or that of the CoCl2â+âastheno group were incubated with 5000 μM YC-1 or 100 nM CoCl2 at 37 â for 60 min, respectively. Health group and Astheno group were not given any of the reagents.
Sperm motility assay
The semen was gently and thoroughly mixed, and then 0.1Â mL of the sample was applied on a slide. A computer-aided sperm analysis system (CASA, ZJ-3000E, Xuzhou, China) was used to analyze sperm concentration and PR (%).
MDC determination for autophagy level of sperms
Semen sample purification
The SWIM-UP method was employed to purify the semen samples. Briefly, a total of 2 mL preheated fallopian tube fluid (HTF, MCE, USA) at 37 â human and 500 μl semen sample were separately added to a centrifuge tube. A clear boundary line between the semen and HTF solution was created so as to segregate the sperms based on their motility. The centrifuge tube was tilted at 45° angle and incubated at 37 â for 1 h.
Experimental procedures of MDC method
Following the instructions of the MDC (Monodansylcadaverin) autophagy staining test kit (Solarbio, China), 875 μl of the supernatant was collected and centrifuged at 700g for 5 min. The cells were dispersed with 1âÃâWash buffer and centrifuged at 800 g for 5 min to collect the cells. The cells were re-suspended in 1âÃâWash buffer, counted, and adjusted to a concentration of 1âÃâ106 cell/mL. A volume of 90 μl of the cell suspension was added into an EP tube and stained with 10 μl of MDC for 30 min in darkness. The cells were then washed with 400 μl of 1âÃâWash buffer and centrifuged. This washing process was repeated twice. The cells were finally re-suspended in 100 μl of collection buffer. A volume of 10 μl of the cell suspension was plated on a glass slide, covered, and observed using a fluorescence microscope (Leica, Germany) with an excitation filter wavelength of 355 nm and a blocking filter wavelength of 512 nm. The autophagy level of the sperm was calculated according to the instructions provided with the kit.
Label-free proteomic experiments
Protein extraction and digestion
The semen sample was combined with lysis buffer (Promega, US) and sonicated for 5 min in an ice bath. The lysis buffer consisted of 8M urea (GibcoBRL, US), 30Â mM HEPES (AMRECSO, US), 1Â mM PMSF (AMRECSO, US), 2Â mM EDTA (AMRECSO, US) and 10Â mM DTT (Promega, US). Subsequently, the samples were centrifuged at 20,000g for 30 min. The supernatant, along with 10Â mM DTT, was incubated at 56Â â for 1 h and then mixed with 55Â mM IAM (Promega, US), followed by incubation in darkness for 1 h. After centrifugation at 20,000g and 4Â â for 30Â min, the protein concentration was determined using the Bradford method.
Once protein extraction was completed, digestion was performed. 40 μg of protein from each sample was transferred to a 3K ultrafiltration tube and centrifuged at 14,000g and 4 â for 40 min. Then, 200 μl of 50 mM NH4HCO3 was added to the sediments and centrifuged again. This process repeated twice. Next, 1 μg/μL trypsin was added to the sample at a protein substrate to enzyme ratio of 30:1, and the mixture was incubated in a water bath at 37 â for 24 h. After the digestion solution was lyophilized, the peptide segments were re-suspended in 30μL 25 mM NH4HCO3.
Mass spectrometry detection and data processing
The Q-Exactive mass spectrometer (Thermo Q Exactiveâ¢, US) was utilized to detect the peptide signals of each purified sample. The liquid phase and mass spectrometry detection parameters were as follows:
Mass spectrometry detection-nanoliter LC column and mobile phase: NanoLC trap: Acclaim PePmap 100, 150 μmâÃâ2 cm nanoviper C18 5 μm 100à ; NanoLC column: C18 5μm 75 μmâÃâ15 cm aperture 300à ; Solvent A: 0.1% formic acid 2% CAN 98% water; Solvent B: 0.1% formic acid (Huayi, China) 2% water 98% CAN (Fisher Scientific, US); Flow rate: 0.4 μl/min.
Mass spectrometry detection-nanoLC liquid phase gradient: B liquid ratio and time: 2% (0Â min), 2% (6Â min), 35% (95Â min), 95% (105Â min), 95% (115Â min), 2% (115.1Â min), 2% (120Â min).
Mass spectrometry detection-Q-E mass spectrometer parameters: Polarity: positive ion mode, MS scan range: 350â1350Â m/z, Resolution: 60,000, Capillary temperature: 350 degrees, Ion source voltage: 2200Â V, MS/MS acquisition modes: Higher collision energy dissociation (HCD), Normalized collision energy (NCE): 38.
After mass spectrometry scanning, the mass spectrometry raw file was obtained. MaxQuant software (https://www.maxqda.com/, version: 1.6.0.1) was applied for data input, screening and quantitative analysis of the raw files. The screening parameters, retrieval and quantitative parameters are detailed below.
Spectrum screening parameters: precursor ion mass range: 350â6000Â Da; minimum peak number in MS/MS spectrum: 10; signal-to-noise ratio (S/N threshold): 1.5.
Identification retrieval parameters: MaxQuant; Fixed modification: Carbamidomethyl (C); Variable modification: Oxidation (M), GlnâââPyro-Glu (N-term Q); Peptide tol: 15ppm; MS/MS tol: 20mmu; Max missed cleavages: 1; Enzyme: Trypsin; Database: Uniprot_human, Number of sequences: 204,703.
Quantitative parameters: Protein ratio type and Normalisation method: Intensity; Minimum peptides: 1.
The significance of protein differences was evaluated using MSstats variance analysis in R software (http://www.rrsoftware.com/, version 4.1.0). The criteria for screening differentially expressed proteins were as follows: (1) The fold change in protein average abundance was greater than 1.2 or less than 0.83, and (2) The p-value of T-test was less than 0.05.
Detection of related protein using ELISA
The semen sample was adjusted to a cellular concentration of 1âÃâ106 cell/mL with PBS (pH 7.2â7.4). After undergoing several cycles of freezing and thawing, 0.5 mL of lysis solution was added to lyse the cells on ice. The mixture was then centrifuged to collect the proteins, and the concentration of total protein was measured with Bradford method.
The levels of glutathione synthetase in the semen samples were determined using the Human Glutathione Synthetase ELISA Kit (Ruichuang, Shanghai, China). Following the kitâs instructions, varied concentrations of standard samples (50 μL each) were added into the standard wells. Blank wells (without samples and enzyme conjugate) and test sample wells were also prepared. In the test sample wells on the coated plate, 40 μL of sample diluent was added first, followed by the addition of 10 μL of the test sample (resulting in a final dilution factor of 5). The samples were placed at the bottom of the plate wells, ensuring no contact with the well walls, and gently mixed. Enzyme conjugate (100 μL) was added to each well (except the blank ones). The plate was sealed with a sealing film and incubated at 37°C for 60 min. After carefully removing the sealing film, the liquid was discarded, and the plate was tapped to remove water droplets. Each well was filled with washing buffer, and then dried. Next, 50 μL of reagent A and 50 μL of reagent B were added in each well. The plate was gently shaken to mix the contents and incubated at 37 °C in darkness for 15 min for color development. Subsequently, 50 μL of stop solution was added to terminate the reaction (turning the color from blue to yellow). The absorbance (OD value) was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm, with the blank well used for zero calibration. The measurement was performed within 15 min after adding the stop solution. The concentrations of the samples were calculated using the linear regression curve equation derived from the standard samples.
Similar operations were followed for the detection of HIF-1α (Jinpin, Shanghai, China), LC3B (Chutai, Shanghai), ENO1 (Xinweiyu, Shanghai,), PGK1 (spbio, Wuhan, China), Cathepsin L (balb, Beijing), and Histone H4 (FineTest, Wuhan, China) using their respective ELISA kits.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 25.0 and GraphPad Prism 8.0 were used for data analysis. The normality test was performed on various basic information variables of all semen samples, including age, abstinence days, sperm concentration, sperm PR, sperm autophagy, and expression of related proteins. Based on the distribution characteristics of the data, multiple linear regression was applied to analyze the relationship between sperm forward motility and related factors. Other statistical methods included analysis of variance (ANOVA), paired sample t-test, rank sum test, chi-square test.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital, Guilin Medical University. Signed informed consents were obtained from the subjects.
All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.